Liposuction: Types, Risks, Prevention, Treatment A
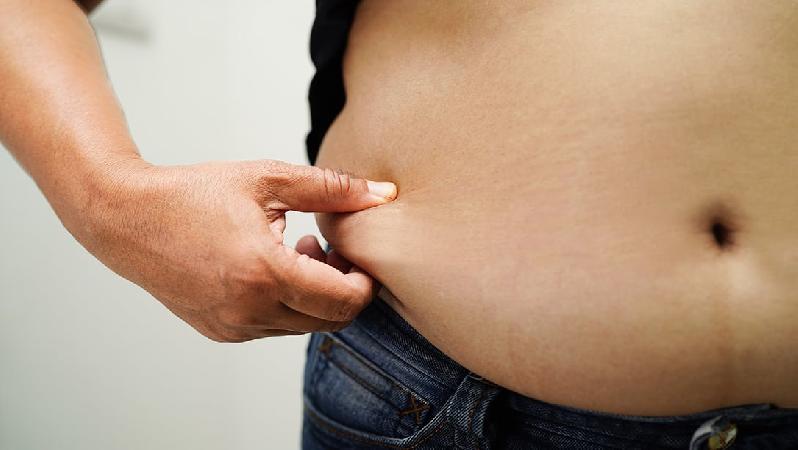
Liposuction is a type of cosmetic surgery. It removes unwanted excess fat to improve body appearance and to smooth irregular body shapes. The procedure is sometimes called body contouring.
Liposuction may be useful for contouring under the chin, neck, cheeks, upper arms, breasts, abdomen, buttocks, hips, thighs, knees, calves, and ankle areas.
Liposuction is a surgical procedure with risks, and it may involve a painful recovery. Liposuction can have serious or rare fatal complications. So, you should carefully think about your decision to have this surgery.
TYPES OF LIPOSUCTION PROCEDURES
Tumescent liposuction (fluid injection) is the most common type of liposuction. It involves injecting a large amount of medicated solution into the areas before the fat is removed. Sometimes, the solution may be up to three times the amount of fat to be removed). The fluid is a mixture of local anesthetic (lidocaine), a medicine that contracts the blood vessels (epinephrine), and an intravenous (IV) salt solution. Lidocaine helps numb the area during and after surgery. It may be the only anesthesia needed for the procedure. Epinephrine in the solution helps reduce loss of blood, bruising, and swelling. The IV solution helps remove the fat more easily. It is suctioned out along with the fat. This type of liposuction generally takes longer than other types.
Super-wet technique is similar to tumescent liposuction. The difference is that not as much fluid is used during the surgery. The amount of fluid injected is equal to the amount of fat to be removed. This technique takes less time. But it often requires sedation (medicine that makes you drowsy) or general anesthesia (medicine that allows you to be asleep and pain-free).
Ultrasound-assisted liposuction (UAL) uses ultrasonic vibrations to turn fat cells into liquid. Afterward, the cells can be vacuumed out. UAL can be done in two ways, external (above the surface of the skin with a special emitter) or internal (below the surface of the skin with a small, heated cannula). This technique may help remove fat from dense, fiber-filled (fibrous) areas of the body such as the upper back or enlarged male breast tissue. UAL is often used together with the tumescent technique, in follow-up (secondary) procedures, or for greater precision. In general, this procedure takes longer than the super-wet technique.
Laser-assisted liposuction (LAL) uses laser energy to liquefy fat cells. After the cells are liquefied, they can be vacuumed out or allowed to drain out through small tubes. Because the tube (cannula) used during LAL is smaller than the ones used in traditional liposuction, surgeons prefer using LAL for confined areas. These areas include the chin, jowls, and face. A possible advantage of LAL over other liposuction methods is that energy from the laser stimulates collagen production. This may help prevent skin sag after liposuction. Collagen is the fiber-like protein that helps maintain skin structure.